Call Today: 916-259-1868
In the rapidly evolving landscape of automation and precision engineering, the concept of a magnetic linear drive has emerged as a pivotal technology, redefining how linear motion is achieved across various applications. Renowned expert in advanced drive systems, Dr. Emily Carter, emphasizes its significance, stating, "A magnetic linear drive not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes wear and tear, making it an ideal choice for high-precision tasks." This statement encapsulates the core advantages that magnetic linear drives offer, from their robust performance capabilities to their longevity in demanding environments.
As industries strive for greater automation and reduced operational costs, the magnetic linear drive stands out due to its unique mechanism that leverages magnetic fields for seamless linear motion. This innovative approach eliminates the need for traditional mechanical components like screws and belts, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and higher reliability. With applications ranging from robotics to CNC machinery, the versatility of magnetic linear drives is a testament to their growing importance in modern engineering solutions. By exploring the workings and applications of this technology, one can appreciate how it is shaping the future of motion control.

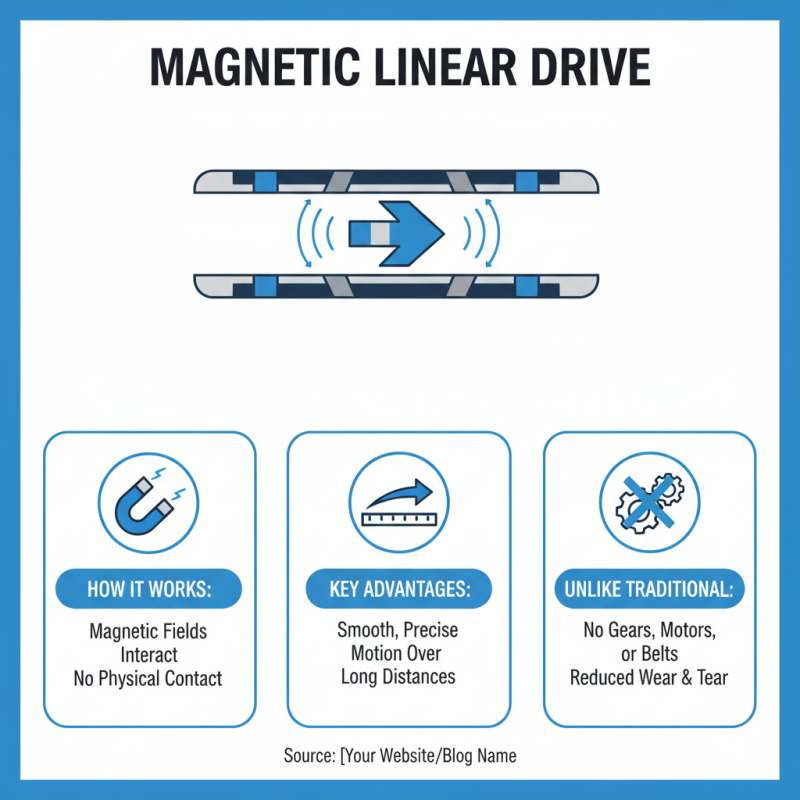
A magnetic linear drive is a type of linear actuator that utilizes magnetic forces to create motion. Unlike traditional drives that rely on mechanical components like gears and motors, magnetic linear drives function through the interaction of magnetic fields. This technology offers a mechanism that is capable of providing smooth and precise motion over long distances without the need for physical contact between moving parts, which minimizes wear and tear.
The core principle behind a magnetic linear drive involves the use of permanent magnets or electromagnets arranged in a specific manner. These magnets interact with a linear guideway fitted with a corresponding magnetic field. When electrical energy is applied, it generates a controlled magnetic field that propels the moving magnet along the guideway, resulting in linear motion. This setup allows for high-speed operation, excellent control, and reduced energy consumption, making magnetic linear drives suitable for a variety of applications, including automation systems, conveyor technology, and robotics. Their design also facilitates easy integration into complex systems, allowing for more versatile engineering solutions.
Magnetic linear drives utilize the principles of magnetism and electromagnetism to create linear motion without the need for mechanical components such as gears and cams. At the heart of their operation is the interaction between magnetic fields produced by coils and permanent magnets. When electrical current flows through the coils, it generates a magnetic field that interacts with the field of the permanent magnets. This interaction creates a force that propels the attached object along a predetermined linear path.
The efficiency of magnetic linear drives stems from their design, which minimizes friction and wear. As the coils are mounted on a stationary rail while the permanent magnets are attached to a moving platform, the absence of contact between these two components significantly reduces maintenance needs and increases operational lifespan. Additionally, these drives can achieve high speeds and precise positioning, making them ideal for applications in automation, robotics, and material handling. By modulating the current through the coils, the speed and direction of the linear movement can be finely controlled, enabling a wide range of industrial applications.
Magnetic linear drives have emerged as a pivotal technology in various industrial applications, primarily due to their efficient and precise motion control capabilities. Central to their operation are several key components. First, the magnetic coils generate a magnetic field, which interacts with permanent magnets or ferromagnetic materials along the drive path. The careful arrangement of these components allows for seamless motion and exceptional load handling, making them ideal for applications requiring high acceleration and deceleration rates.
Another crucial element is the control system, which oversees the performance of magnetic linear drives. Advanced algorithms enable precise positioning and speed regulation, resulting in increased operational efficiency. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global market for linear motion systems, which includes magnetic linear drives, is projected to reach $12.2 billion by 2025, highlighting the growing adoption of this technology across various sectors, including robotics, manufacturing, and material handling. The rise in automation demands further emphasizes the importance of reliable and responsive linear drive systems, reaffirming the role of their key components in driving technological advancements.
| Component | Description | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Track | A surface that provides the magnetic field for linear motion. | Automated guided vehicles, conveyor systems |
| Magnetic Levitation Element | Allows for frictionless movement by suspending the load without contact. | High-speed trains, precision equipment |
| Drive Coil | Generates the electromagnetic force to propel the linear motion. | Robotic arms, linear actuators |
| Control System | Manages the operation and coordination of the drive components. | Industrial automation, CNC machines |
| Feedback Sensors | Provide data on position and speed to maintain accuracy. | Robotics, material handling systems |
Magnetic linear drives are essential components in various industries, providing precise and reliable motion control. These drives utilize magnetic fields to enable linear movement without the need for mechanical contact, resulting in reduced wear and tear. Common applications of magnetic linear drives include automation in manufacturing, robotics, and material handling systems. In the automotive industry, they are employed for assembly line automation, improving efficiency and reducing production downtime.
In addition to manufacturing, magnetic linear drives have found a significant role in the healthcare sector. They are used in surgical robots and diagnostic equipment, where precision and reliability are paramount. The pharmaceutical industry also benefits from their application, as magnetic linear drives facilitate the automated packaging and labeling of medication, ensuring accuracy and compliance with regulations.
Tip: When selecting a magnetic linear drive for your application, consider the load requirements and the environment in which it will operate. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and potential interference from other electronic devices can impact performance. Always consult with engineers to ensure optimal integration. Additionally, regular maintenance checks can prolong the lifespan and efficiency of these systems.
Magnetic linear drives offer distinct advantages that make them increasingly popular in various applications. One of the most significant benefits is their ability to provide smooth, quiet motion without the need for mechanical linkages, reducing wear and maintenance costs. These drives utilize magnetic fields to create linear motion, enabling precise positioning and high-speed operation. Their contactless nature results in less friction, which not only prolongs the lifespan of the system but also enhances energy efficiency. This feature is particularly valuable in industries where noise and maintenance downtime can impact productivity, such as in automation or materials handling.
However, magnetic linear drives also come with limitations that must be considered when evaluating their feasibility for specific applications. One major drawback is their sensitivity to external magnetic fields, which can interfere with their performance and accuracy. Additionally, the complexity of the control systems required to operate these drives can lead to higher initial costs. In certain environments, such as those with high temperatures or corrosive substances, the materials used in magnetic drives may not withstand the conditions, potentially limiting their applicability. Thus, while magnetic linear drives present numerous advantages, understanding their limitations is crucial for effective implementation in diverse operational settings.
This chart illustrates the performance metrics of Magnetic Linear Drives. The metrics include High Speed, Precision, Efficiency, Cost, and Complexity, with values ranging from 0 to 100, representing relative performance in applications.






Sierramotion engineers help customers design solutions to complex motion problems. Whether a simple coil, or a precision motion assembly working in vacuum, Sierramotion has the experience to create a solution that works the first time.