Call Today: 916-259-1868
In the rapidly evolving landscape of automation and robotics, understanding the mechanics behind technologies like the linear motion motor is essential. As defined by industry expert Dr. Emily Chen, a professor of mechanical engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, “The linear motion motor is a game-changer in how we approach precision and efficiency in movement-based applications.” This statement underlines the significance of linear motion motors in modern engineering, where they serve as a pivotal component in various industries, including manufacturing, transportation, and healthcare.
Linear motion motors operate on the principles of converting electrical energy directly into linear motion, eliminating the need for complex gear systems. Their unique design allows for high-speed performance, precise control, and reduced maintenance requirements, which are crucial in high-demand settings. As technologies advance, the role of linear motion motors is becoming increasingly crucial in ensuring that systems function with optimal efficiency, making them an indispensable part of contemporary machinery.
As industries continue to seek innovative solutions for faster and more reliable operations, the linear motion motor stands out as a vital technology that embodies the future of mechanical design. With advancements in materials and control systems, the capabilities of these motors will only expand, further revolutionizing automation practices across various sectors.

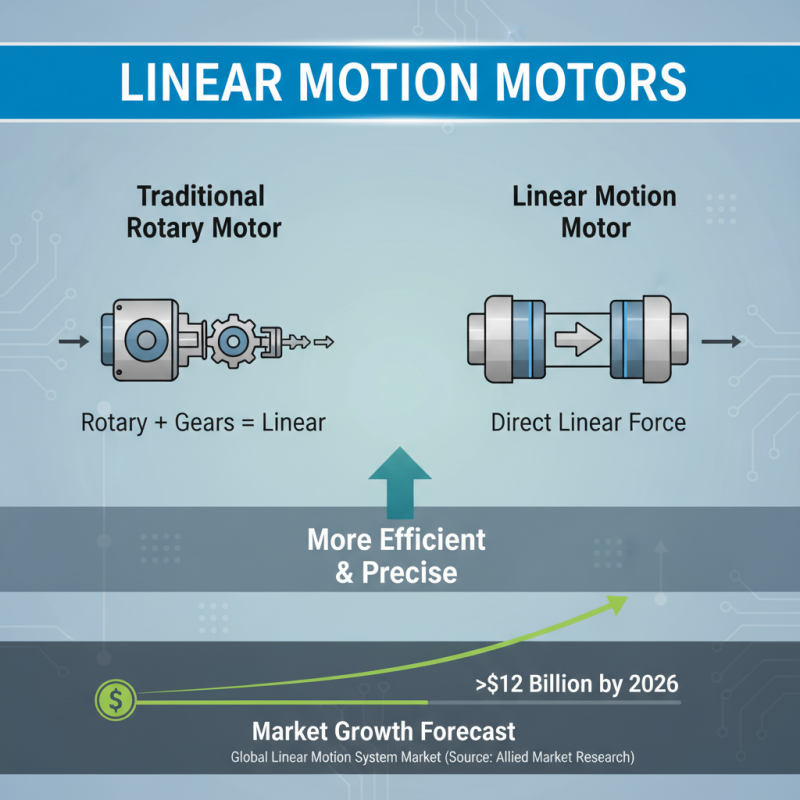
Linear motion motors are advanced electromechanical devices designed to convert electrical energy into linear motion. Unlike traditional rotary motors that require additional mechanical components like gear systems to achieve linear movement, linear motion motors directly produce linear force, allowing for more efficient and precise operations. According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global linear motion system market is expected to reach over $12 billion by 2026, indicating a significant growth driven by various applications in automation and robotics.
These motors utilize electromagnetic principles, where the interaction between magnetic fields and electric currents produces linear force. In various industrial applications, including CNC machining, material handling, and assembly lines, linear motion motors offer advantages such as high speed, acceleration, and modularity. Industry experts from Technavio project that the demand for linear motion products will expand by over 8% annually due to increasing automation in manufacturing processes, which underscores the relevance of these systems in contemporary industrial settings.
Linear motion motors are a type of electric motor that produces linear motion directly from electrical energy without the need for intermediate mechanical components such as gears or belts. The operation of these motors is based on the principles of electromagnetic forces. When an electric current flows through a coil, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with magnets positioned along a fixed track. This interaction generates a linear force that drives the mover along the length of the motor. According to a report by Markets and Markets, the linear motion control market is expected to grow from $9.6 billion in 2020 to $14.3 billion by 2025, indicating a significant increase in demand for these systems across various industries.
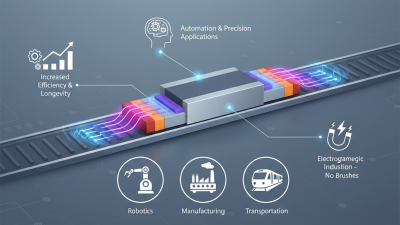
The functionality of linear motion motors can be understood through two primary types: contact and contactless motors. Contact motors, such as voice coil motors, operate with direct contact between components, while contactless motors utilize magnetic levitation, eliminating wear and improving longevity. An analysis from Research and Markets highlights that contactless linear motors are gaining traction due to their enhanced precision and reduced maintenance requirements, making them ideal for applications in robotics, automated assembly, and even medical devices. Overall, the unique operation principles of linear motion motors present a compelling advantage for multiple high-tech applications where precision and efficiency are paramount.
Linear motion motors are increasingly used in various industries due to their unique capabilities and efficiencies. The prevalent types include linear induction motors, linear synchronous motors, and linear reluctance motors. Each type operates on distinct principles, catering to specific applications. For instance, linear induction motors are favored in transportation systems, such as maglev trains, due to their ability to move large masses over long distances with minimal friction. According to a report by Research and Markets, the linear motor market is projected to reach USD 6.5 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.5% from 2021.
In manufacturing, linear synchronous motors are instrumental in automation processes. These motors enable precise positioning and high-speed movement of equipment such as conveyor belts and robotic arms. The global shift towards automation and Industry 4.0 has contributed to the increased adoption of these motors, as highlighted in a study by Mordor Intelligence, which noted that the automation sector is expected to grow significantly, driving demand for efficient linear motion solutions. Additionally, linear reluctance motors are emerging in applications requiring robust and reliable drive systems, such as electric vehicles and aerospace, showcasing their versatility and increasing relevance across multiple sectors.
This chart displays the number of units sold for different types of linear motion motors, showcasing their applications in various industries.
A linear motion motor is a device designed to produce linear motion directly from electrical energy. It operates based on principles of electromagnetism and is composed of several key components that work in tandem to achieve movement. Understanding these components is crucial in grasping how linear motion motors function effectively.
One of the primary components of a linear motion motor is the stator. This is the stationary part that includes coils of wire which create a magnetic field when an electric current flows through them. The stator is typically designed to generate a consistent magnetic field that interacts with the moving parts of the motor. Another essential component is the moving part, often referred to as the actuator or slider. This component is equipped with magnets that respond to the magnetic field produced by the stator, allowing it to move in a straight line with great precision and speed.
Additionally, linear motion motors may include other elements such as bearings and guides which help to stabilize and direct the motion of the actuator. These components ensure that the movement remains smooth and accurate, reducing friction and wear. The integration of these various elements allows linear motion motors to be used in a wide range of applications, from robotics to automation technologies, highlighting their versatility and efficiency in providing linear movement.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Stator | The stationary part of the motor that generates a magnetic field. | Provides the magnetic force necessary to move the rotor. |
| Rotor | The moving part of the motor that interacts with the stator's magnetic field. | Converts electrical energy into linear motion. |
| Coils | Wound wires that create a magnetic field when electricity flows through them. | Induces movement in the rotor through electromagnetic forces. |
| Control System | The electronic circuitry that regulates motor function. | Manages power supply and movement precision. |
| Guide Rails | Tracks that direct the motion of the moving components. | Ensures stable and accurate linear movement. |
Linear motion motors offer several advantages that make them a popular choice in various applications. One of the primary benefits is their ability to provide smooth and precise linear motion without the need for intermediate mechanical components like gears or belts, which can introduce friction and wear over time. This direct drive capability results in improved accuracy and faster response times, making linear motion motors ideal for applications that require high-speed movement and tight tolerances, such as robotics and automation systems.
However, linear motion motors also have limitations that must be considered. One significant drawback is their cost; they can be more expensive compared to traditional actuators and motors. Additionally, the complex control systems required to operate these motors may necessitate advanced programming and specialized knowledge, potentially complicating setup and maintenance. Furthermore, linear motion motors might have limitations in their force output and the range of motion, which can restrict their use in certain heavy-duty applications where more power is necessary. Understanding these advantages and limitations is crucial for engineers and designers when selecting the appropriate motion control technology for their specific needs.



Sierramotion engineers help customers design solutions to complex motion problems. Whether a simple coil, or a precision motion assembly working in vacuum, Sierramotion has the experience to create a solution that works the first time.