Call Today: 916-259-1868
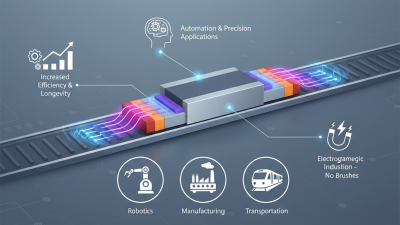
Understanding tubular linear motors can be enlightening. These motors feature a unique structure that offers enhanced performance. They operate efficiently in various applications, including robotics and transportation.
Despite their advantages, many people struggle with their complexity. This guide aims to simplify the learning process. It provides key insights into how tubular linear motors work. You'll discover important factors such as design, efficiency, and applications.
Many misunderstand the potential of these motors. Some think they are outdated technology, but that's far from the truth. Embracing the nuances of tubular linear motors can lead to innovation. As you read on, reflect on your own perceptions and knowledge gaps.

Tubular linear motors are fascinating devices. They convert electrical energy into linear motion. This makes them unique. Their structure consists of a cylindrical shape, which helps in efficient movement. The design allows for smooth operation in various applications.
Understanding how these motors work is crucial. They utilize electromagnetic fields to generate force. The motion occurs in a straight line, unlike rotary motors. This feature makes them ideal for precise positioning tasks. Many industries rely on this technology for automation. Manufacturing systems often benefit from their speed and accuracy.
However, there are challenges to consider. Installation can be complex, affecting performance. Maintenance is often required to ensure longevity. Users may face difficulties when integrating them into existing systems. These factors need thoughtful consideration. A deep understanding of their functionality is essential for maximizing efficiency.
| Tip Number | Tip Description | Key Components | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Understand the basics of linear motion principles. | Magnet, Coil, Frame | Industrial automation, Robotics |
| 2 | Learn how electromagnetic principles apply. | Current, Magnetic Field, Force | Medical equipment, Conveyors |
| 3 | Explore various types of tubular motors. | Single-phase, Multi-phase | Packaging, CNC machines |
| 4 | Review the importance of cooling systems. | Heat sinks, Fans | High-speed applications |
| 5 | Understand control systems for operation. | Drive controllers, Sensors | Automation systems |
| 6 | Learn about performance metrics. | Speed, Acceleration, Torque | Precision movements |
| 7 | Address alignment and installation challenges. | Mounting fixtures, Calibration tools | Assembly lines |
| 8 | Assess the environmental factors affecting performance. | Temperature, Humidity | Outdoor applications |
| 9 | Look into maintenance routines to enhance durability. | Lubrication, Inspections | Manufacturing |
| 10 | Study the future trends in tubular linear motors. | Smart technologies, IoT integration | Advanced robotics |
Tubular linear motors are becoming increasingly popular for their unique design and functionality. Understanding their key components is essential for effective application. The main component, the tubular stator, houses the winding. This part interacts with the moving rotor, which contains magnets. Together, they create motion when electrical current flows through the windings. This design allows for a compact and streamlined construction.
Another important aspect is the coil arrangement. The way coils are placed affects performance and efficiency. A well-structured coil design can improve the motor's power output. However, not all configurations are ideal. It's crucial to analyze different coil arrangements and their implications.
Cooling systems also play a critical role. Maintaining optimal temperature is essential for performance. Overheating can lead to efficiency loss and damage. Often, engineers must reflect on their cooling strategy to optimize motor life. Lastly, the mounting options must be carefully considered. Improper mounting can lead to misalignment, affecting performance. It's vital to ensure appropriate support for the best results.
This chart represents the performance metrics of tubular linear motors based on various key components. It highlights the relationship between efficiency, torque, and speed that are critical in understanding the performance of these motors.
Tubular linear motors operate on the principles of electromagnetic induction. They utilize a long, cylindrical rotor that moves within a stationary stator. The design allows for efficient force generation and minimal friction. According to industry reports, these motors can achieve thrust forces up to 1,000 N, making them suitable for various applications.
The unique structure of tubular linear motors enables a compact design. This feature is beneficial in applications where space is limited. The linear motion they provide is smooth and precise. However, there can be challenges with heat generation during operation. Excessive heat may lead to reduced performance and lifespan.
Another consideration is the integration of these motors into existing systems. Adapting to tubular linear motors requires careful planning and design modifications. While their benefits are clear, the transition may not be seamless. Industry data indicates that up to 30% of projects face delays due to integration issues. Understanding these factors is crucial for successful implementation.

Tubular linear motors have transformed various industries through their efficient design. These motors deliver high performance in applications where precise movement is critical. In manufacturing, they play a vital role in automation. Robotics systems leverage tubular motors for accurate positioning and repeated tasks. This increases productivity and reduces errors on the assembly line.
In the automotive sector, tubular linear motors are used in electric vehicles and advanced driver-assistance systems. They provide rapid response times, enhancing safety and efficiency. However, the balance between power and size in motor design can be challenging. Engineers often face trade-offs to achieve optimal performance.
Healthcare equipment also benefits from tubular linear motors. They are used in surgical tools and diagnostic devices, where precision is paramount. Yet, ensuring reliability and durability in these sensitive environments can be complex. Continuous innovation and testing are essential to address these issues.
Tubular linear motors have gained attention in various industries due to their unique design and capabilities. These motors are compact and efficient. However, they also come with distinct advantages and limitations that engineers must consider. According to a report by the International Electromechanical Society, tubular motors often provide better thrust density compared to traditional linear actuation systems. They can deliver high force output in a smaller size, making them ideal for applications like robotics and automation.
On the downside, the cost of tubular linear motors can be a significant barrier. Initial investment tends to be higher compared to other motor technologies. This discourages some users from adopting this innovative solution. Additionally, the complexity of the control system can pose challenges. Precise positioning often requires advanced feedback systems, which can complicate the setup. Some users report that maintenance can also be difficult, leading to longer downtimes.
Furthermore, environmental factors may limit their application. Tubular motors are sensitive to temperature and humidity variations. This sensitivity can affect performance in uncontrolled environments. Users must think critically about these aspects before implementation. Though tubular linear motors offer remarkable benefits, these limitations must be addressed for successful integration into existing operations.



Sierramotion engineers help customers design solutions to complex motion problems. Whether a simple coil, or a precision motion assembly working in vacuum, Sierramotion has the experience to create a solution that works the first time.